Sampurna Geography - Geography for UPSC IAS Civil Services Exam - PMF IAS
Map of India - Geography of India: An Introduction - Civils daily
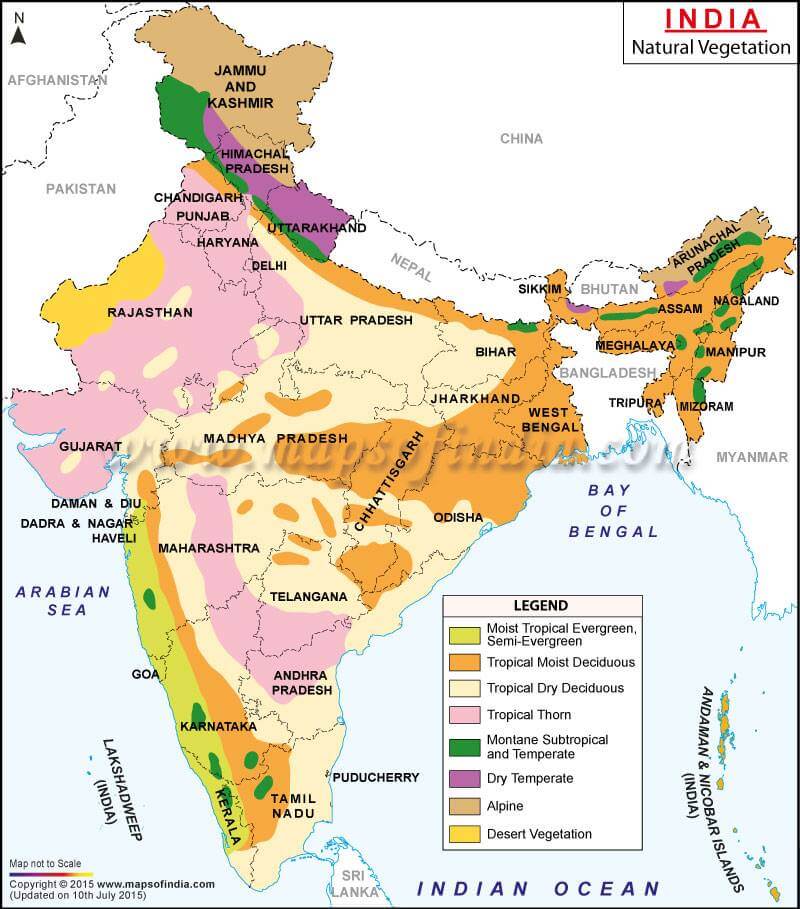
- Types and Characteristics
- PMF IAS
- State wise vegetation in India.
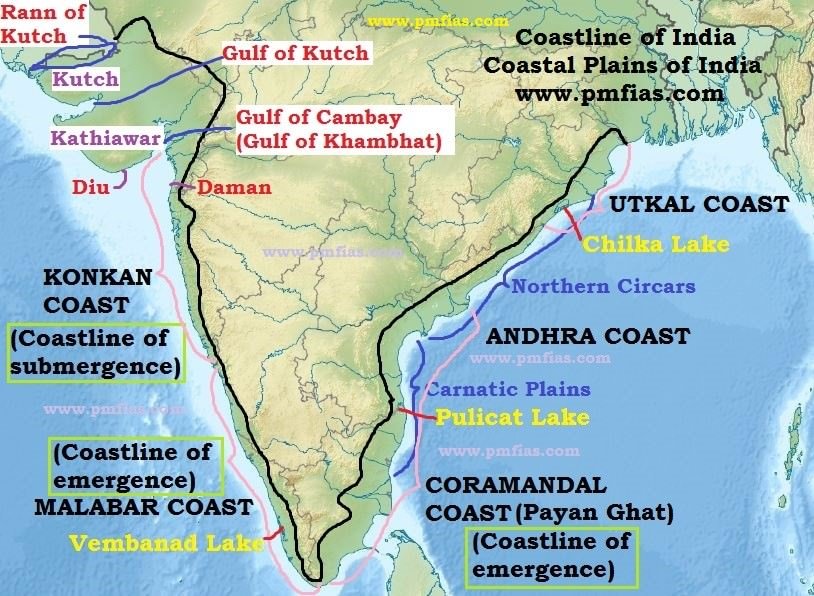
Division of India's Costal Region
Thermal Power Station
- Thermal Power Plant in India
- Dul Hasti Power Station
- Maitri Super Thermal Power Project
- Singareni Thermal Power Plant
- The problems plaguing Thermal Power Generation
- Kothagudem - AP
- Raichur - KN
- Mettur - TN
- Wanakbori - Gujarat
Hydroelectricity Power Project
- Hydro electricity in Himalayas
- Impact of Hydro power electricity in Himalayan Region
- Ratle Hydroelectricity Project
- Shanan Power Project
- Suban Siri Lower Hydroelectric Project
- War Hydroelectric Project
- Hydropower Potential in India
- Arun 3 Hydro Project
- Mentioned in PYQs
- Tapovan (Chamoli district of Uttarakhand)
- Vishnugarh (Same)
- Tehri Hydropower complex - Bhagirathi river
- Vishnugadh Pipalkoti Hydroelectricity Project - Alaknanda river
- Tapovan Vishnugadh Hydropower Project - Dhauliganga
Irrigation Project
- Irrigation Projects and Schemes
- Access to assured Irrigation
- Irrigation Benefit Types and Efficiency
- Available ground water available of states in sequential manner.
- Ground water resource assessment report
- Status of ground water in India
- Per capita water availability
- Extraction of Ground water
- Mentioned in PYQs
- Damanganga (Gujarat)
- Gima (Jalgaon area of Maharashtra)
- Pamba (Kerala)
- Multipurpose River Valley Project in India
- Same BYJU'S
- Multipurpose Project in India
- Sapt Kosi High Dam Project
- Dibang Multipurpose Project
- Omkareshwar Project (World's largest floating solar project) - Narmada river
Nuclear Power Plant
Important Dams (River, Forest cover - Biosphere reserve, National Park, WLS etc.)
- Tehri Dam
- Koteshwar Dam
- Nizam Sagar Dam
- Gandhi Sagar Dam - Chambal
- Kosi Project
- Damodar Valley Project
- Bhakhra Nangal Project
Nuclear Power Plant
- Koodankulam
Hills of the peninsular India (Origin of Rivers, Correct sequence of hills)
- Mahabaleshwar
- Badrinath
- Amarkantak
- Nasik
- Anna Mudi - Highest peak in the Western Ghats
- Nilgiri area
- Toda live in Nilgirs area
Mountain Passes
Wetlands
- Theory
- Ramsar sites in India
- Ramsar Convention on wetlands and Montrex record
- Important wetlands PYQs
- Harike wetlands
- Keoladeo Ghana NP
- Kolleru lake
- Compare state wise wetlands.
- Largest Inland saline wetlands - Rajasthan
- Iron and Steel Industry
- Raw Material - Iron ore, Coal, Limestone etc.
- Impurities
- Silicon ==> small quantity ==> deoxidizing agent ==> good.
- Sulphur ==> Brittle ==> Reduce strength ==> Very bad.
- Phosphorus - Affect ductility and resistance to shock - Very bad.
- Lead ==> Improve machinability ==> small quantity good.
- Manganese ==> Most effective deoxidant ==> Good effect on Sulphur
- Tin ==> Form low melting point brittle film => Make steel very useless
- Oxygen ==> Bad influence property of steel.
- Input in Iron blast
- Ore ==> iron ore
- Fuel ==> coke
- Flux ==> limestone
- Destructive distillation ==> Coal is cooked to produce coke (90-93% carbon).
- Output - Liquid slag, Pig iron (Liquid iron) and gases.
- Role of Limestone = Remove Sulphur
- Pig Iron ==> Fe (93-95%) + Si + S + Mg + P + Ti + C (all in small quantity)
- Caste Iron = C(<2%) + Si ==> Automotive industry parts, cast iron pan.
- Steel = C > 2.1%
- Stainless steel = Chromium (min 5%) + Ni + Mn + Molybdenum
- Wrought iron
- Made by mixing liquid iron with some slag.
- Much lower carbon content
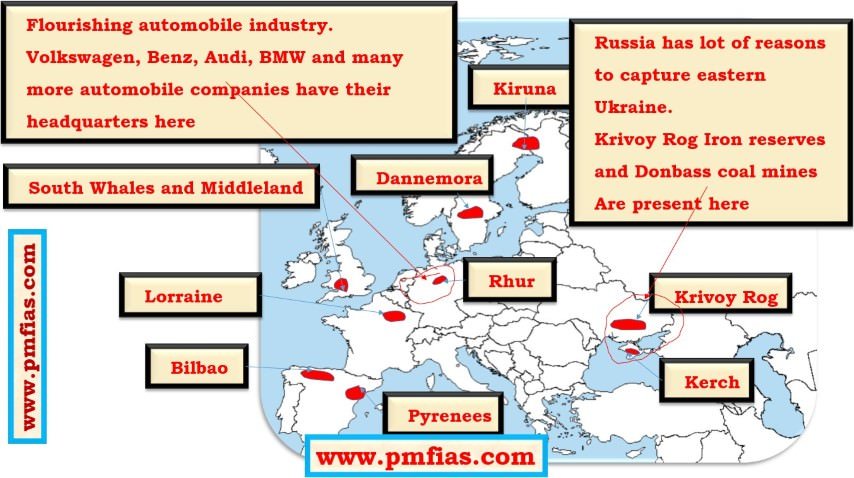
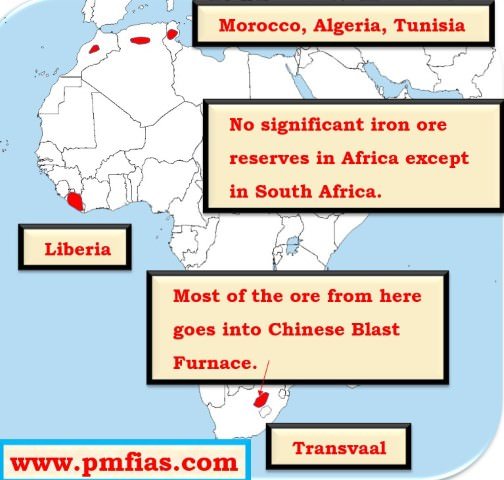
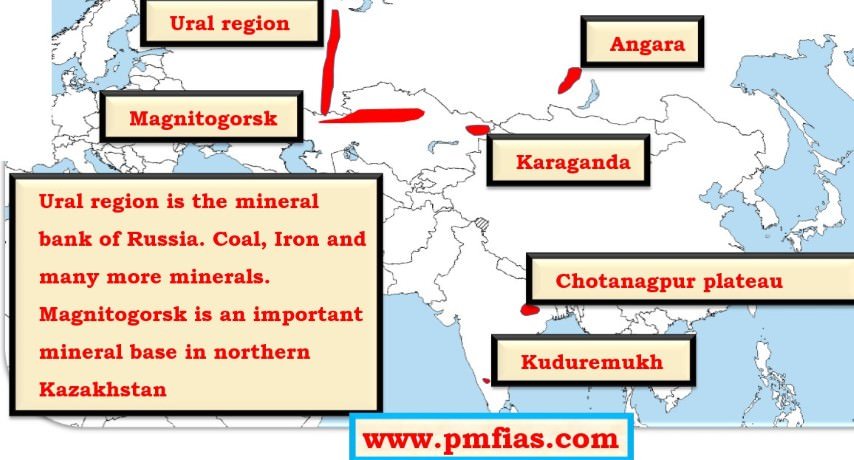
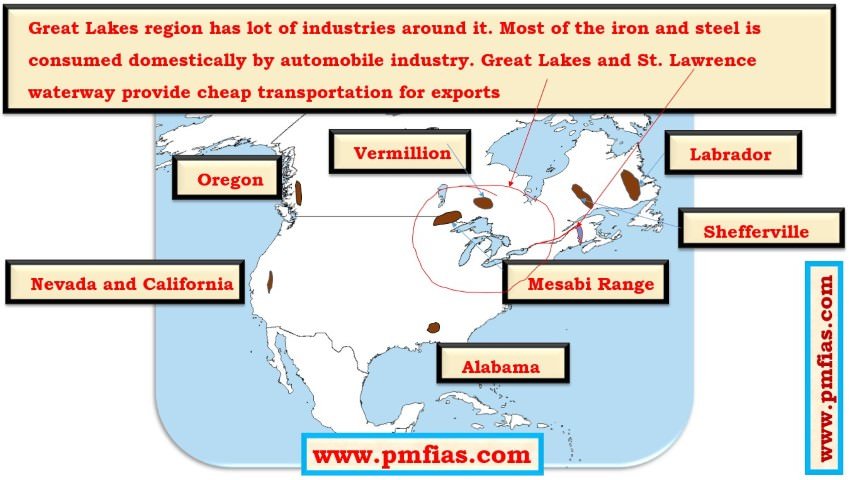
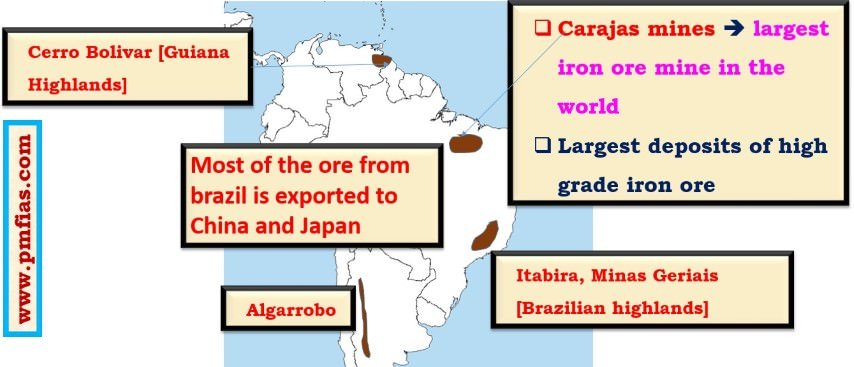
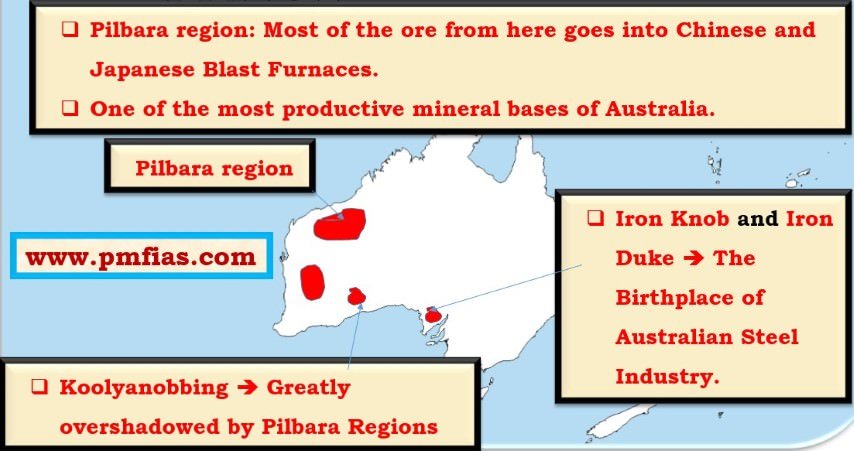
- Distribution of Iron ore across the world.
Manganese
- Most important Mn ore is pyrolusite.
- Primarily used in Iron and Steel Industries.
- Basic raw material for manufacturing of alloys.
- 6 Kg of Mn ore is required for manufacturing of one tons of steel.
- Also used in manufacturing of bleaching powder, insecticides, paints and batteries.
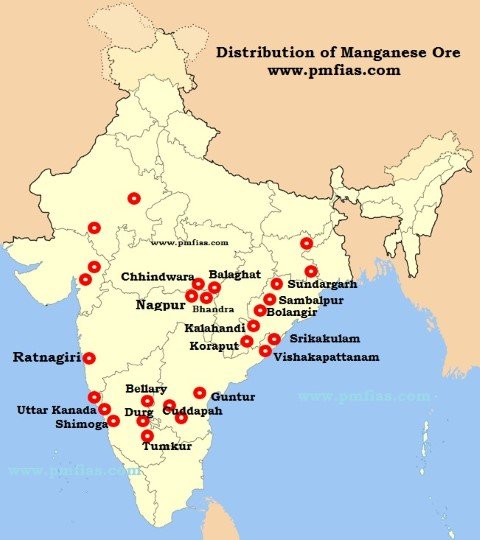
State wise reserves - Odisha > Karnataka > Madhya Pradesh > Maharashtra > Andhra Pradesh > Jharkhand and Goa > Rajasthan, Gujarat, and West Bengal.
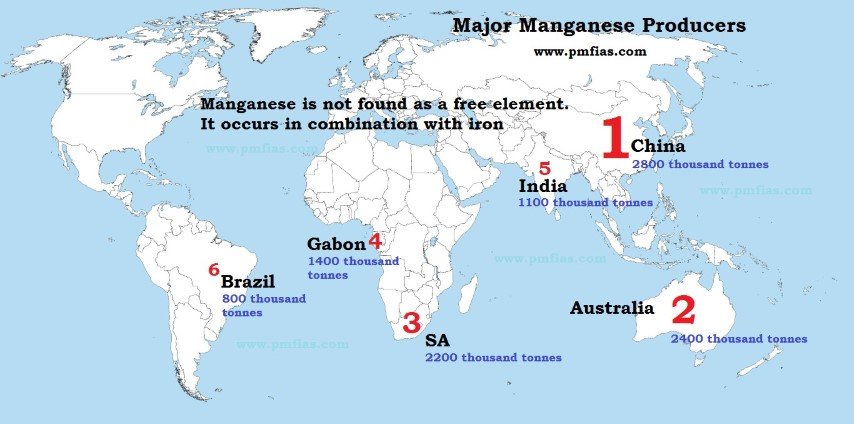
- India second largest reserves after Zimbabwe.
- Fifth largest producers after China, Gabon, South Africa and Australia.
- Maharashtra (27.66%) - Nagpur and Bhandara district, Ratnagiri Hills.
- MP (27.59%) - Balaghat and Chhindwara district
- Odisha (24%) - 1st in reserve but 3rd in production
- Gondite deposite (Sundargarh district)
- Kodurite and Khondolite deposits in Kalahandi and Koraput district.
- Lateritic deposits in Bolangir and Sambalpur district.
- Andhra Pradesh (13%)
- Srikakulam and Vishakhapatnam district.
- Cuddapah, Vijayanagaram and Guntur districts.
- Karnataka (6%) - Uttara Kannada, Shimoga, Bellary, Chitradurg and Tumkur district.
- Other producers
- Goa
- Panchmahal and Vadodara in Gujarat.
- Udaipur and Banswara in Rajasthan.
- Singhbhum and Dhanbad district in Jharkhand.
Export of Manganese
- 4/5th total production consumed domestically.
- Export decreasing - Increasing domestic demands.
- Japan largest buyer.
- Other buyers - USA, UK, Germany, France, Norway.
- Chromium - Copper - Nickel
- Bauxite - Lead-Zinc - Tungsten - Pyrite
- Dolomite
- Tin
- Asbestos
- Coal
- Gold
- Mica, Limestone and other Non-Metallic Minerals
- Graphite
- Lead
- Salt
- Silver
- Bentonite
- Chromite
- Kyanite
- Sillimanite
- Feldspar
- Tungsten
- Quartz
- Magnesium
- Diamond
- Zinc
- Diamond bearing kimberlite - Raipur
Energy Minerals
- Coal
- Namchik Namphuk coal field - Arunachal Pradesh
- Uranium
- Natural Gas
- Shale Gas
- Cavery basin (Mehsana, Ahmedabad and Bharuch district of Gujarat)
- Cambay basin (Nagapattinum Tamil Nadu)
- Krishna-Godavari basin (East and West Godavari district of Andhra Pradesh)
- Petroleum
Important Acts
- MMDR Act 1957
- India Forest Act 1947
- Scheduled Tribe and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of forest rights) Act 2006
- Forest Conservation Act 1980
- Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Environment Conventions and Protocols
- Minor Minerals
- Sand
- Large nonmetallic and Non energy minerals fall under minor category.
- Major Minerals - Metallic Minerals are mostly in the major minerals category.
- Minor forest produce
- Major forest produce
Major Industrial Location
- Industrial Region in India
- Distribution of Major Industries - Location factors
- Woolen textile
- Aluminum
- Fertilizer
- Cement
- Iron and Steel
Maharatnas, Navratna and Miniratnas
Important Industrial Towns
- Badrachalam
- Chanderi
- Kancheepuram
- Karnal
Name of Islands and their Significance
- Tipis
- Barkhans
- Phoomdis
- Izba
National Park - Location, Topography, River, Climatic zones, Natural vegetation
- Manas National Park
- Namdapha National Park
- Neora Valley National Park
- Valley of Flower National Park
- Corbett National Park
- Kaziranga National Park
- Silent Valley National Park
- Nilgiris hills
- Pathrakkadavu Hydroelectric Project
- Kunthi river
- Chandra Prabha - Varanasi
- Karera - Jhasi
- Jaisamand - Udaipur
- Nahargarh - Jaipur
- Bondala Wildlife Sanctuary - Goa
- Kangerghat National Park - Chandigarh
- Orang Sanctuary - Assam
- Ushkothi Wildlife Sanctuary - Odisha
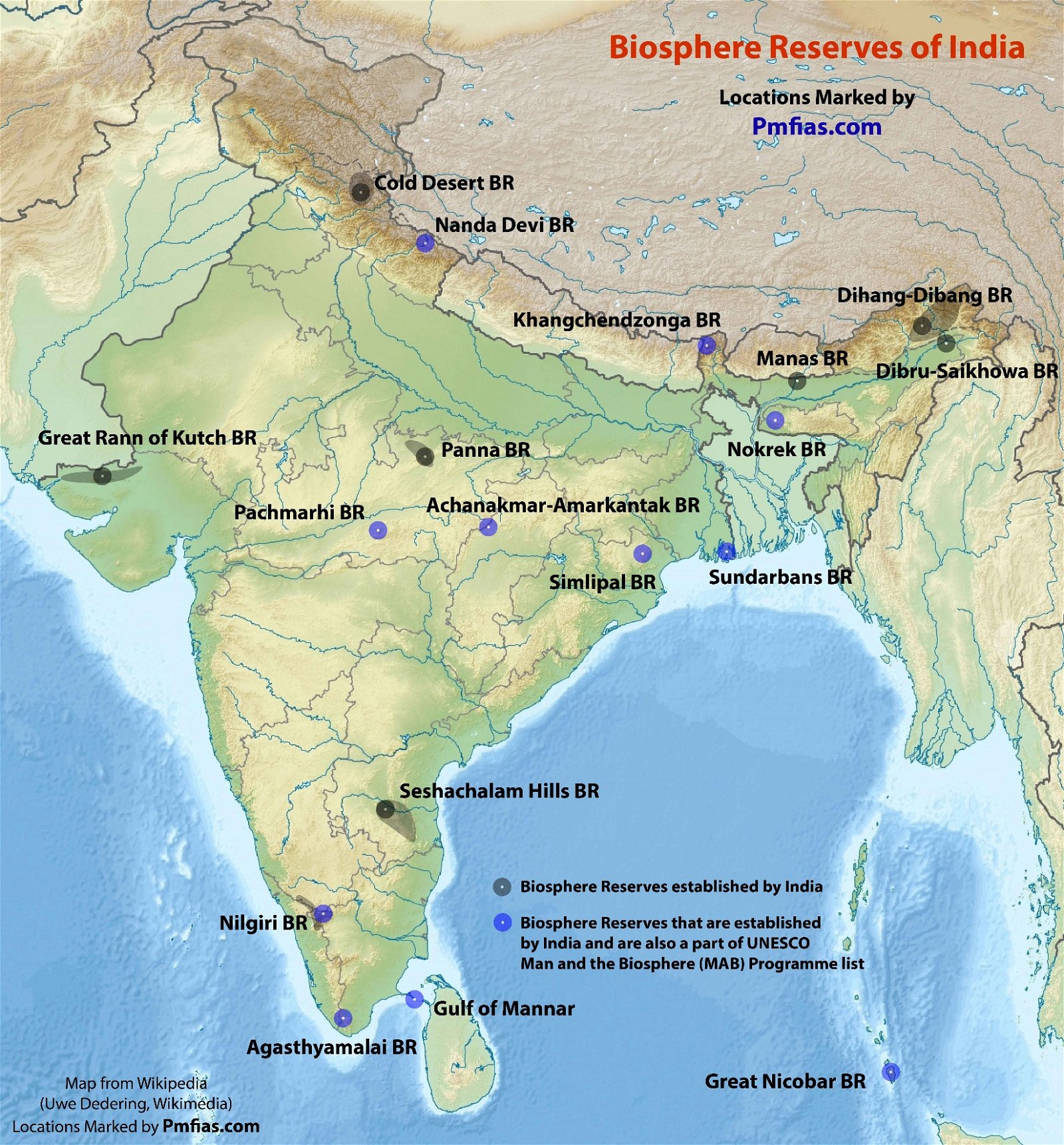
UNESCO World Heritage Site
- Champaner - Pavagadh - Archeological Site
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Railway Station
- Mahallapuram
- Sun Temple (Konark Temple)
- Complete List
Lakes / Dam in India
- Kodaikanal (TN) - Artificial Lakes
- Kolleru (Andhra P)
- Nainital (UK)
- Renuka (HP)
- Govind Sagar
- Ukai Reservoir
- Wular Lake
Indian Sericulture
- Oak Tasar Silk
State wise ranking for Ground water Resources for Irrigation
Mineral Oils
Atomic Mineral Division of Department Atomic Energy
Population densityLanguage spoken in different states and region in India.
State wise Population of Schedule Tribe
National Highway
National Highway
Ports in India (Major and Minor ports)
- Kakinada
- Karwar
- Mangalore
- Tuticorin
- Veraval
- Mahe
- Pondicherry
- Yanam
- Karaikal
- Kochi
- Dahej
- Paradip
- New Mangalore
- Region on Map
India's Population
Time Zones - Calculating local time of particular place following their longitude and latitude.
River Map - Origin - Dam - Irrigation project - Canals - Conservation reserve - Flora and Fauna - Important Tributaries (Learn with correct sequence)
- Indus and their tributaries
- Kosi
- Gomati
- Ghaghara
- Gandaki
- Teesta
- Krishna
- Cavery
- Godavari
- Tungabhadra
- Damodar
- Mahanadi
- Yamuna
- Chambal
- Ganga
- Son
- Chandrabhaga
- Malaprabha
- Vamsadhara
- Indiravati
- Pranhita
- Pennar
- Barak
- Lohit
- Subansiri
- Brahamputra
- Manas
- Pagladia
- Puthimari
- Dhansiri
- Jia Bharati
- Subansiri
- Irewaady
- Mekong
- Luni
- Narmada
Important Valley
- Markha Valley - Jammu Kashmir
- Dzukou Valley - Nagaland
- Sangla Valley - Himachal Pradesh
- Yamthung Valley - Sikkim
Waterfalls
- Kapildhara falls (Narmada)
- Jog falls (Sharavathi river)
- Shivasamudram falls (Cavery)
8-, 9- and 10-degree channels
Predominant Language of different regions
- Brajbhasha
- Bhojpuri
- Maithili
- Awadhi
Tree Species
- Teak
- Deodar
- Sandalwood
- Sundari
- Sal
- Oak
- Rhododendron
- Juniper (Himalayan Region)
- Mahogany (Carribean, Central and South America}
- Islver fir (Himalayan Region)
- Spruce (Himalayan Region)
Wild life
- Lion
- Tiger
- Elephant
- One horned Rhinoceroses
- Cheetah
- Coral Reefs
- Mollusca
- Dolphins
- Tortoise
- Salt water crocodile (Andaman and Nicobar Island)
- The Great Indian Bustard
- Various sea birds
- Shrew and Tapir (Western ghats of Malabar region)
- Red Panda (Mountains of Nepal, North-eastern India, China, Bhutan)
- Slow Loris (Dense forest of North east and Assam)
Protected Area Network
- Bhitarkanika
- Desert National Park
- Eravikulam, Kerala
Area under forest cover - Percentage of forest cover in total area in state.
- Maharastra < Madhyapradesh < Odisha < Chattisgarh
Major Topography of India
- Rift valley region
- Chhattisgarh plain
- Rain shadow region
- Chota Nagpur Plateau
Races
- Australoid race
- Caucasoid race
- Mongoloid race
- Negroid race
Major tribes in India (Region and State)
- Miri
- Konyak
- Apatani
- Lambada
- Buksa
- Kol
- Munda
- Korba
- Changpa
- Semi nomadic Tibetan ethnic group
- Zanskar region of Jammu Kashmir
- Rear Pashmina goat
- Kept in category of ST
- Shompen tribe - One of two mongoloid tribe found in Nicobar Island.
- Other tribes found in
- Nilgiri hills
- Nicobar Island
- Spiti Valley
- Lakshadweep Island
States (Forest cover, Crop production, Climate, Protected Area Network)
Recently discovered something
- Sundarbans
- Kerala Coast
- Orissa Coast
- Andaman and Nicobar Island
- Jurassic Land Mass
- Aryavart
- Indiana
- Gondwana Continent
- Ravva offshore block
- Krishna - Godavari basin
- Cavery basin
- Mahanadi Basin
- Palar Pennar Basin
- Aliyar - (Tamil Nadu)
- Isapur- Maharashtra
- Kangsabati - West Bengal
- Underground Cave System


Comments
Post a Comment